About GravityView Caching
A quick way to fetch uncached data when accessing a View's is by adding the ?cache parameter to the end of the URL where your View is located. Example: https://example.com/view/directory/<strong>?cache</strong>
What GravityView Caches
Caching entry requests reduces the number of queries performed on a page load by hundreds and possibly thousands when dealing with large View. This makes GravityView faster.
GravityView caches entry requests for Views to speed up the plugin. Requests are cached using a unique key generated on the specific request details, including the current page number, the number of results, and the sorting values.
When data changes in a Gravity Forms form, all caches using that form data are cleared. This way, caches do not result in out-of-date data being displayed.
Cached results are stored in the WordPress options table, similar to the Transients API.
DataTables Extension
In addition to caching the entries query, GravityView caches the JSON responses used by the DataTables Extension. This allows the request to be processed faster, which is important for the responsiveness of the extension.
What happens when entries are added or changed
When an entry is created or modified in Gravity Forms, the GravityView cache adds the entry's form to a list of forms that have been changed, the "cache blocklist".
The cache blocklist is stored in WP Options table with the name of gravityview_cache_blocklist .
When entries for a View are fetched, GravityView checks whether the View is connected to a form on the cache blocklist.
If the requested form is on the blocklist, then:
- The cached entries are cleared from all Views connected to the form
- The form is removed from the blocklist
- The cache returns false so that a new query will be used to fetch entries
All these processes are logged for easy debugging using the Debug Bar plugin.
Clearing expired caches
Because GravityView stores caches in "transients", they are only cached for a set amount of time (default: one day).
Each request is cached separately, including each page of each View. This can add up to many database entries, so twice a day, GravityView runs a script that deletes expired caches.
Setting the cache globally
You can set the default cache for all Views by going to GravityKit Settings screen: In the GravityKit menu, go to Settings. Click on the GravityView tab, and you will see the Caching section. Here you define default caching that will apply to new Views.
If "Enable Caching" is toggled on, the Entry Cache Duration setting will appear. This is where you can specify the default cache duration ("lifetime") in seconds. The default setting is 86400: one day.
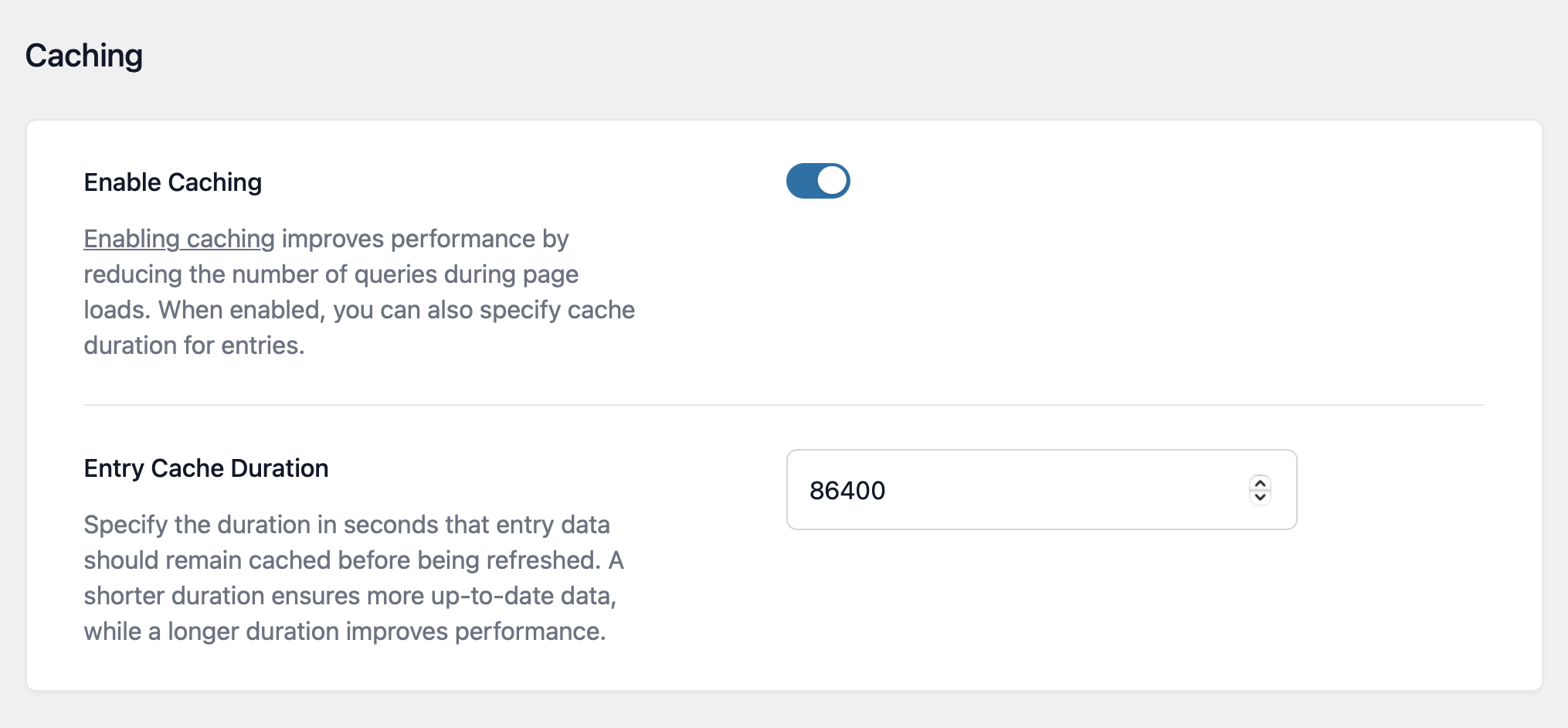
Global caching settings also apply to Views that existed before GravityView Version 2.20 and have not been saved since upgrading.
Setting the cache for a single View
When editing a View, you can modify or disable caching by changing the "Enable Caching" View setting. You will find the setting when editing a View in the Settings box under "View Settings".
When the global cache is enabled, the View will be cached by default. Uncheck the "Enable Caching" checkbox to override the default and disable caching for a View.

How to temporarily disable the cache
If you are logged in and you can edit posts, you can temporarily disable the cache by adding ?cache or ?nocache . This will disable the cache for that request.
Disable cache with a filter
You can also disable the cache permanently by adding the code snippet below on your website. This filter overrides the global and View cache settings.
add_filter('gravityview_use_cache', '__return_false');
Read here how to add these code samples to your website: Where to put code samples.
GravityView Cache Filters
You can use the following filters to modify the cache functionality:
gravityview_use_cache(boolean) Whether to use GravityView caching. Default:true. Second parameter: is the currentGravityView_Cacheobject.gravityview_cache_time_{$filter_name}(int) Number of seconds to cache requests. Default:86400(1 day in seconds).$filter_nameis the parameter when setting the cache value. Filter names include:gravityview_cache_time_entries- Entries fetched usinggravityview_get_entries()gravityview_cache_time_datatables_output- DataTables JSON response
gravityview_cleanup_transients(boolean) Enable or disable GravityView automatic cleanups of expired caches. Default:true
_1@2x.png)